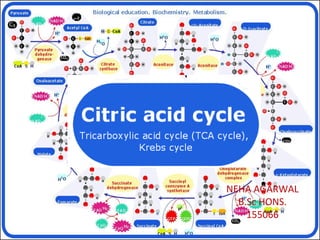
Citric Acid Cycle: An Overview of Key Reactions and Regulation
- 2. Glucose Glucose-6- phosphate Pyruvate Glycogen Ribose, NADPH Pentose phosphate pathway Synthesis of glycogen Degradation of glycogen Glycolysis Gluconeogenesis LactateEthanol Acetyl Co AFatty Acids Amino Acids The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules — amino acids, fatty acids, and carbohydrates. Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A.
- 3. In eukaryotes the reactions of the citric acid cycle take place inside mitochondria Hans Adolf Krebs. Biochemist; born in Germany. Worked in Britain. His discovery in 1937 of the ‘Krebs cycle’ of chemical reactions was critical to the understanding of cell metabolism and earned him the 1953 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine.Physiology or Medicine.
- 4. An Overview of the Citric Acid Cycle A four-carbon oxaloacetate condenses with a two-carbon acetyl unit to yield a six-carbon citrate. An isomer of citrate is oxidatively decarboxylated and five-carbon α- ketoglutarate is formed. α-ketoglutarate is oxidatively decarboxylated to yield a four-carbon succinate. Oxaloacetate is then regenerated from succinate. Two carbon atoms (acetyl CoA) enter the cycle and two carbon atoms leave the cycle in the form of two molecules of carbon dioxide. Three hydride ions (six electrons) are transferred to three molecules of NAD+ , one pair of hydrogen atoms (two electrons) is transferred to one molecule of FAD. The function of the citric acid cycle is the harvesting of high-energy electrons from acetyl CoA.
- 6. 1. Citrate Synthase Citrate formed from acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate Only cycle reaction with C-C bond formation Addition of C2 unit (acetyl) to the keto double bond of C4 acid, oxaloacetate, to produce C6 compound, citrate citrate synthase
- 7. 2. Aconitase • Elimination of H2O from citrate to form C=C bond of cis- aconitate • Stereospecific addition of H2O to cis-aconitate to form isocitrate aconitase aconitase
- 8. 3. Isocitrate Dehydrogenase • Oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to a-ketoglutarate (a metabolically irreversible reaction) • One of four oxidation-reduction reactions of the cycle • Hydride ion from the C-2 of isocitrate is transferred to NAD+ to form NADH • Oxalosuccinate is decarboxylated to a-ketoglutarate isocitrate dehydrogenaseisocitrate dehydrogenase
- 9. 4. The α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Complex • Similar to pyruvate dehydrogenase complex • Same coenzymes, identical mechanisms E1 - a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (with TPP) E2 – dihydrolipoyl succinyltransferase (with flexible lipoamide prosthetic group) E3 - dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (with FAD) α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
- 10. 5. Succinyl-CoA Synthetase • Free energy in thioester bond of succinyl CoA is conserved as GTP or ATP in higher animals (or ATP in plants, some bacteria) • Substrate level phosphorylation reaction HS-+ GTP + ADP GDP + ATP Succinyl-CoA Synthetase
- 11. • Complex of several polypeptides, an FAD prosthetic group and iron- sulfur clusters • Embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane • Electrons are transferred from succinate to FAD and then to ubiquinone (Q) in electron transport chain • Dehydrogenation is stereospecific; only the trans isomer is formed 6. The Succinate Dehydrogenase Complex Succinate Dehydrogenase
- 12. 7. Fumarase • Stereospecific trans addition of water to the double bond of fumarate to form L-malate • Only the L isomer of malate is formed Fumarase
- 13. 8. Malate Dehydrogenase Malate Dehydrogenase Malate is oxidized to form oxaloacetate.
- 15. Stoichiometry of the Citric Acid Cycle Two carbon atoms enter the cycle in the form of acetyl CoA. Two carbon atoms leave the cycle in the form of CO2 . Four pairs of hydrogen atoms leave the cycle in four oxidation reactions (three molecules of NAD+ one molecule of FAD are reduced). One molecule of GTP,is formed. Two molecules of water are consumed. 9 ATP (2.5 ATP per NADH, and 1.5 ATP per FADH2)are produced during oxidative phosphorylation. 1 ATP is directly formed in the citric acid cycle. 1 acetyl CoA generates approximately 10 molecules of ATP.
- 16. • Integration of metabolism. The citric acid cycle is amphibolic (both catabolic and anabolic). Functions of the Citric Acid Cycle The cycle is involved in the aerobic catabolism of carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids. Intermediates of the cycle are starting points for many anabolic reactions. • Yields energy in the form of GTP (ATP). • Yields reducing power in the form of NADH2 and FADH2.
- 17. Regulation of the Citric Acid Cycle • Pathway controlled by: (1) Allosteric modulators (2) Covalent modification of cycle enzymes (3) Supply of acetyl CoA (pyruvate dehydrogenase complex) Three enzymes have regulatory properties - citrate synthase (is allosterically inhibited by NADH, ATP, succinyl CoA, citrate – feedback inhibition) - isocitrate dehydrogenase (allosteric effectors: (+) ADP; (-) NADH, ATP. Bacterial ICDH can be covalently modified by kinase/phosphatase) −α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (inhibition by ATP, succinyl CoA and NADH
- 18. Krebs Cycle is a Source of Biosynthetic Precursors Phosphoenol- pyruvate Glucose The citric acid cycle provides intermediates for biosyntheses