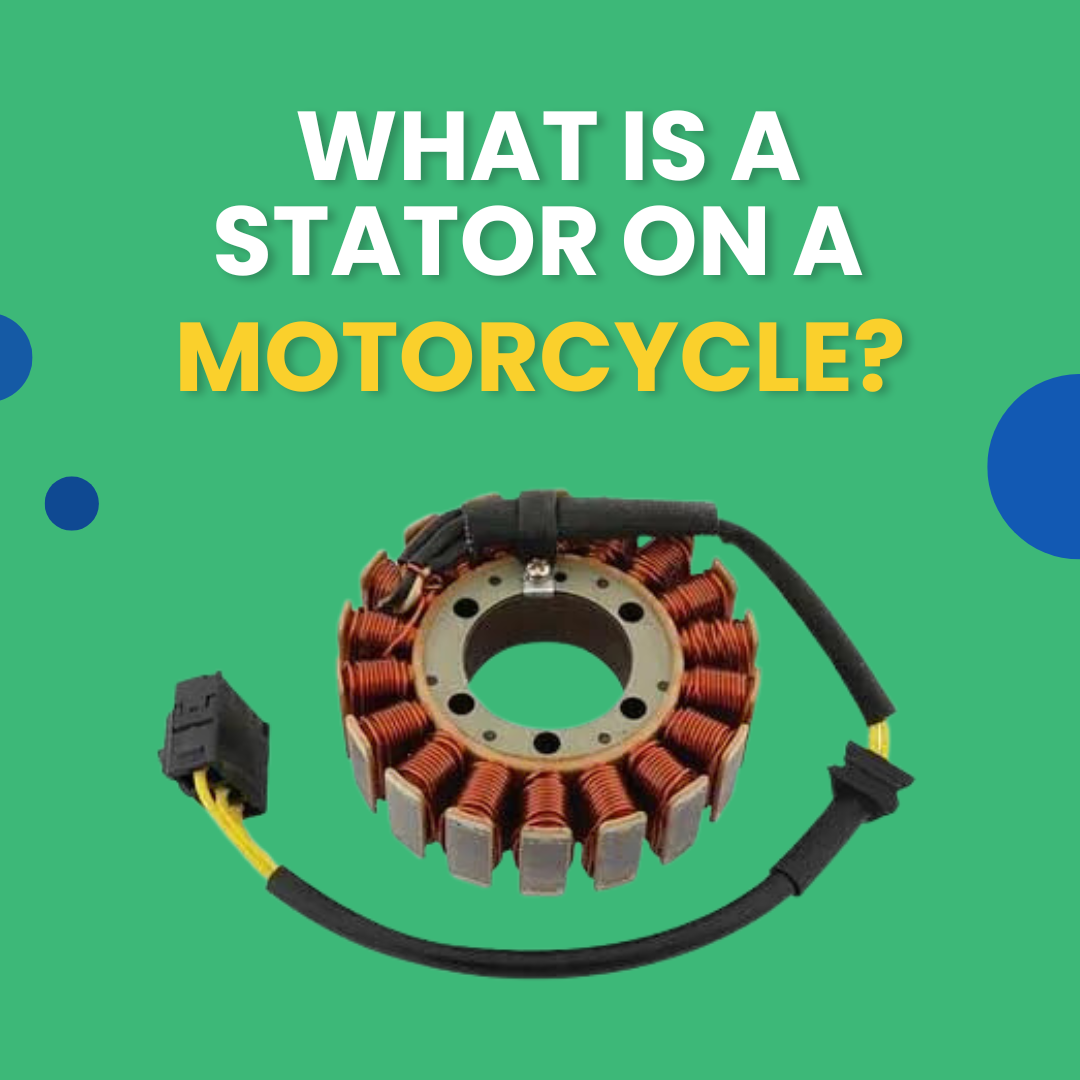
What Is A Stator on A Motorcycle? How Do Stators Work?
Ever had your motorcycle battery die in the middle of nowhere, leaving you stranded?
It's an issue many riders face, and it often stems from a little-known but crucial component of your motorcycle's charging system - the stator.
This mysterious part, hidden away in the heart of your engine, might be small, but it plays a big role. 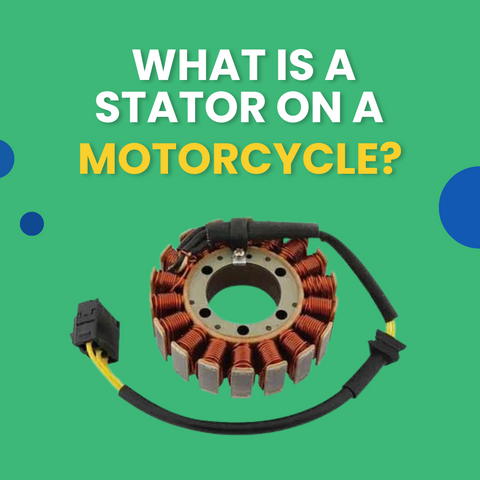
What if you could better understand this essential component, know how to spot the signs of a faulty stator, and even learn how to replace it?
Well, you've come to the right place.
By the end of this article, not only will you understand what a stator is and how it works, but you'll also gain knowledge that could save you from potential roadside headaches in the future.
What is a Stator on a Motorcycle?
Motorcycles, like any other motor-powered vehicle, depend on their electrical system for several crucial functions.
A critical component of this system is the stator. You might be thinking, "What does a stator do on a motorcycle?"
Let's find out!
The Function of a Stator
Working Principle of a Stator
The stator on a motorcycle is part of the charging system and is primarily responsible for generating electrical power.
It uses the mechanical motion already present in the engine to generate this power.
Isn't that amazing?
It’s like getting something from nothing! Now, let's dig deeper into how it works.
It's also useful to note the typical location of a stator in a motorcycle.
Generally, the stator can be found inside the engine casing on the left side of most motorcycles.
Although its precise location may vary depending on the make and model of the bike, it's usually positioned around the flywheel area.
This also applies to our toys and kids petrol motorbikes. We also sell a range of other motorbikes for kids.
Related: How You Can Charge Your Motorcycle Battery Without a Charger
Components of the Stator System
The stator itself is a coil of wire housed inside the engine case. A magnet on a shaft spins within this coil, creating an alternating current (AC).
Now, if we had a pint-sized physics teacher with us, they'd probably remind us of Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
Here, the magnetic field, created by the spinning magnet, induces an electric current in the stator's coil.
In simple terms, motion from the engine spins a magnet which, in turn, generates electricity.
This generated AC power then travels along heavy gauge wire through the case and into a component called the rectifier/regulator.
As you might guess from its name, the rectifier/regulator converts AC power into direct current (DC) power, and ensures the output remains consistent.
Additionally, in the motorcycle world, you might hear the terms "generator," "stator," and "alternator" used interchangeably.
While there are technical differences between these components in broader contexts, when it comes to motorcycles, they essentially serve the same purpose of converting mechanical energy into electrical energy for various bike functions.
If you like riding motorbikes, you may find this article helpful - From Clumsy to Confident: How to Shift Gears on a Motorcycle Like a Pro
Importance of a Stator in a Motorcycle
How does a Stator Charge the Battery?
The stator is crucial for keeping your motorcycle's battery charged. All the electrical stuff on your bike, like lighting, ignition, fuel pump, and starter, relies on power from the battery. And it's the job of the stator to keep the battery juiced up.
So, in a way, the stator is like the life-support system for your bike's battery.
Related: How Long Does It Take to Charge a Motorcycle Battery?
Symptoms of a Bad Stator on a Motorcycle
How do you know when your motorcycle stator is in trouble?
There are a few tell-tale signs.
One of the most common symptoms of a bad stator is difficulty starting the bike.
If the battery is not charging properly, you may find your motorcycle reluctant to start or failing to hold a charge.
Headlights that flicker or seem unusually dim may also indicate a problem with the stator.
Besides the physical symptoms, a failing stator could also impact your pocket.
If your battery continually dies and needs to be replaced, or if you're consuming an unusual amount of fuel, these could be indirect signs of a stator issue.
It's worth getting these checked out as the costs of multiple batteries or the excess fuel can add up over time.
Not to mention the potential damage to other components of your motorcycle's electrical system.
Replacing a Stator on a Motorcycle
If you suspect a bad stator, it's generally best to consult a professional mechanic.
Replacing a stator on a motorcycle can be a tricky process if you're not familiar with the engine's inner workings.
But fear not!
With a bit of guidance, even a novice can tackle this job. The process involves removing the left-side engine cover, replacing the old stator with a new one, and reassembling the components.
Testing a Motorcycle Stator
Testing a motorcycle stator is another way to diagnose a potential issue.
A multimeter, an electrical tool that measures voltage, current, and resistance, can be used to perform this test.
By checking the resistance and output voltage of the stator, you can determine whether it's working properly or needs to be replaced.
Can a Motorcycle Run Without a Stator?
The simple answer?
No, not for long.
A motorcycle can run on a fully charged battery for a short period, but without a functioning stator, the battery will quickly drain.
It's like trying to run a marathon without any food – you might start strong, but you'll soon run out of energy!
In Summary
To wrap things up, the stator is a critical part of your motorcycle, integral to the charging system.
We've learned that it's responsible for transforming the mechanical motion of the engine into electrical energy, keeping your battery charged and all the electrical components on your bike running smoothly.
Spotting the symptoms of a bad stator, understanding its replacement procedure, and knowing its typical location are all part of being an informed rider.
Regular maintenance of your motorcycle's charging system, including the stator, can prevent sudden failures and extend its life.
Remember, a well-maintained motorcycle not only ensures a smoother ride but can also save you from potential troubles and unnecessary costs.
Knowledge is power, especially when it's about a power-generating component like the stator!
FAQs
Are there different types of stators for different motorcycles?
Yes, there are different types of stators for different motorcycles. Single-phase and three-phase stators are both used in motorcycle engines for power generation, and each type provides power differently and has its benefits. The number of spokes or poles on a stator can also vary, with some stators having between four to eighteen spokes or poles arranged in a circle, similar to the spokes on a wagon wheel. The type of stator used in a motorcycle depends on the specific make and model of the bike, as well as the electrical requirements of the bike's components.
How long does a motorcycle stator typically last?
The lifespan of a motorcycle stator can vary depending on several factors, including the make and model of the bike, the electrical requirements of the bike's components, and the quality of the stator itself. Based on the search results, it seems that stator life expectancy can range from as low as 7,000 miles to as high as 45,000 kilometres (28,000 miles) or more (123). Some riders have reported stator failure after only one or two years of use, while others have reported stators lasting for tens of thousands of miles (14). Heat is often cited as a major factor in stator failure, and running a series regulator/rectifier (R/R) can help prolong stator life (5). However, there is no definitive answer to how long a motorcycle stator typically lasts, as it can vary widely depending on the specific circumstances.
Can I use a car battery charger to charge a motorcycle battery drained due to a bad stator?
Yes, it is possible to use a car battery charger to charge a motorcycle battery that has been drained due to a bad stator. However, it is important to ensure that the charger is compatible with the motorcycle battery and that it is used correctly to avoid damaging the battery. Here are some options for charging a motorcycle battery:
- Use a motorcycle battery charger: These chargers are specifically designed for use with motorcycle batteries and are available in a variety of types and brands. They are generally easy to use and can help prolong the life of the battery.
- Use a car battery charger: It is possible to use a car battery charger to charge a motorcycle battery, but it is important to ensure that the charger is compatible with the battery and that it is used correctly. Some motorcycle chargers can also be used on cars, but it is important to check the specifications to ensure that they are suitable for the battery in question.
- Use a trickle charger: Trickle chargers are designed to maintain the charge of a battery over a long period of time and can be used on both cars and motorcycles. They are generally easy to use and can help prolong the life of the battery.
Is it harmful to the engine or any other motorcycle components if I keep riding with a bad stator?
Yes, riding your motorcycle with a bad stator can lead to a number of problems. For one, it can drain your battery, which can cause issues with ignition, lighting, or other electrically powered components. Furthermore, if the battery is not properly charged, it can put excess strain on the engine. It's best to get a suspected bad stator checked and replaced if necessary.

